Exporting Audit Events to Syslogs
In Linux systems, the rsyslog utility is used to generate external logs, and OpenIAM also uses it as an external tool. Rsyslog can work over the network through port 514 using TCP/UDP protocols, which is used to export OpenIAM audit events.
The user can configure rsyslog to listen to TCP and UDP on port 514, and then OpenIAM sends audit logs to the listening port. Rsyslog receives OpenIAM logs on port 514 and adds them to system logs according to the rsyslog configuration.
Below, you can find detailed guidelines on how to set up syslog and use it to export audit events from OpenIAM.
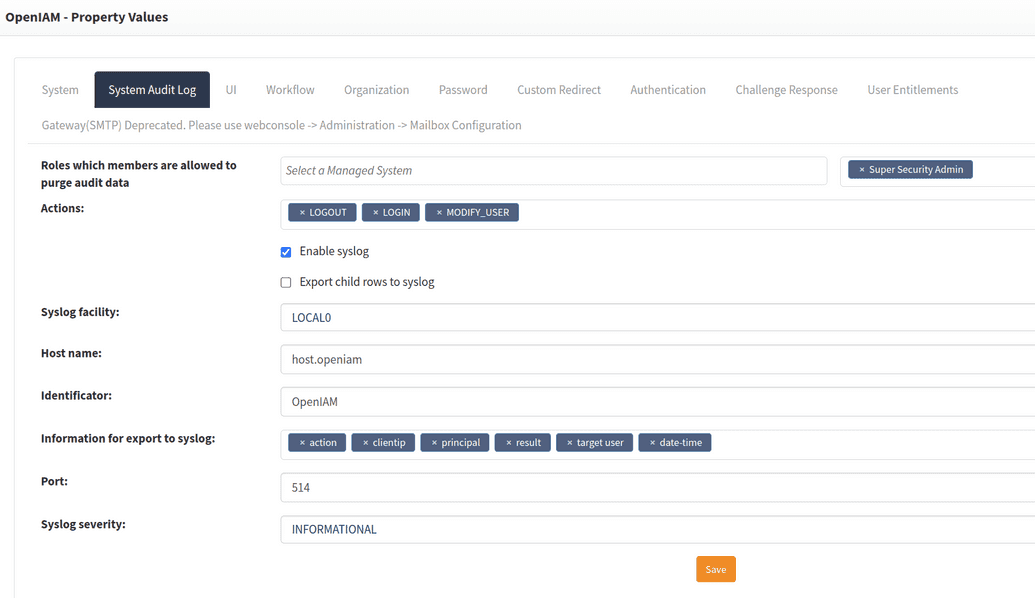
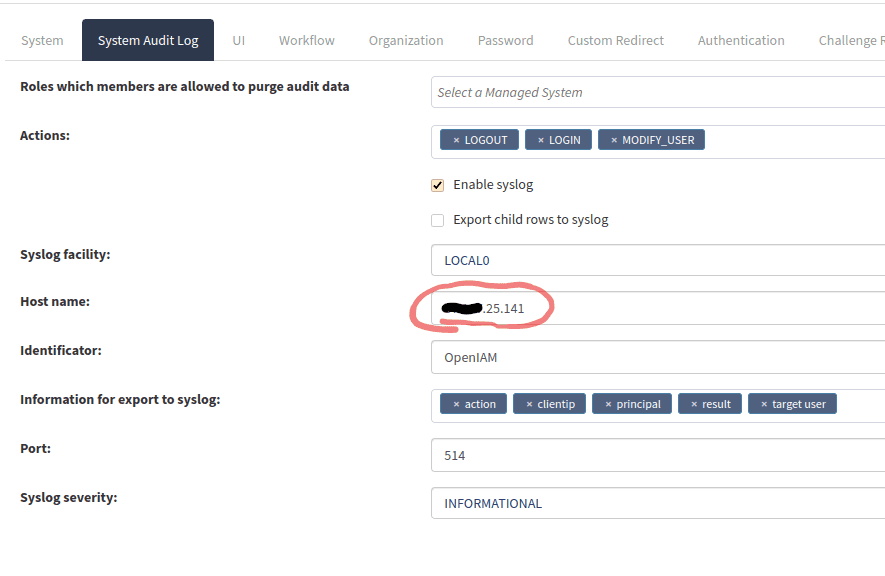
As a first step, users need to use the following properties:
The fields for properties are described below.
| Field | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| Actions | Audit logs actions to add to syslog. | LOGIN, LOGOUT |
| Enable syslog | Turns syslog on/off. | Checked / Unchecked |
| Export child rows to syslog | Allows exporting child rows of the audit log. | On / Off |
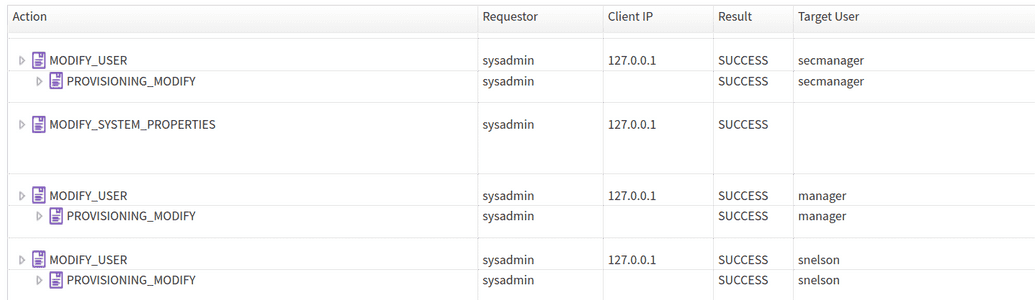
Below you can see an option of having a MODIFYUSER action, which can export to syslog without the _Export child rows to syslog checkbox. But for exporting the PROVISION_MODIFY action, the user needs to check the checkbox.
| Field | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| Syslog facility | The syslog facility name. | LOCAL0 |
| Host name | Host name of the server where syslog is placed. | |
| Identifier | Identifier in syslog | OpenIAM |
| Information for export to syslog | Audit log information which will be added to syslog. |
Example of a string in the system log file:
Jan 11 21:34:25 localhost OpenIAM: Action:[LOGIN] ClientIP:[127.0.0.1] Principal:[sysadmin] Result:[SUCCESS] Targets:[[3000:sysadmin]]
| Field | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| Port | Port of the server where syslog is placed. | |
| Syslog severity | Syslog priorities | Selectable values: (EMERGENCY, ALERT, CRITICAL, ERROR, WARNING, NOTICE, INFORMATIONAL, DEBUG) |
Example of a string in the system log file:
Jan 11 21:34:25 localhost OpenIAM: Action: [LOGIN] ClientIP: [127.0.0.1] Principal: [sysadmin] Result:[SUCCESS] Targets: [[3000:sysadmin]]
Settings for CentOS' syslog:
- To switch on the syslog listener for rsyslog, uncomment:
/etc/rsyslog.conf
Provides UDP syslog reception
$ModLoad imudp$UDPServerRun 514
Provides TCP syslog reception
$ModLoad imtcp$InputTCPServerRun 514
- For each log facility, a different log file can be used, for example:
/etc/rsyslog.confif $syslogfacility-text == 'local1' then /var/log/local1
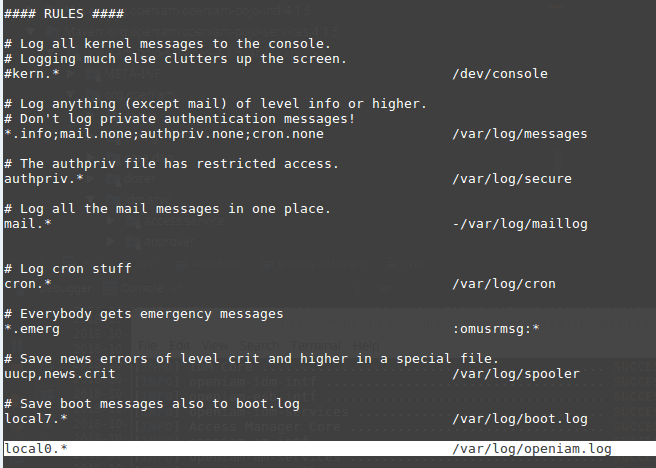
Otherwise, you can set the required output file for the exact facility by adding a rule to the conf file:
/etc/rsyslog.conf →local0.* /var/log/openiam.log
- To redirect to another server:
- Over UDP 514, add to /etc/rsyslog.conf a line like
. @192.168.10.99
- Over TCP 514, add to /etc/rsyslog.conf a line like
. @@192.168.10.99
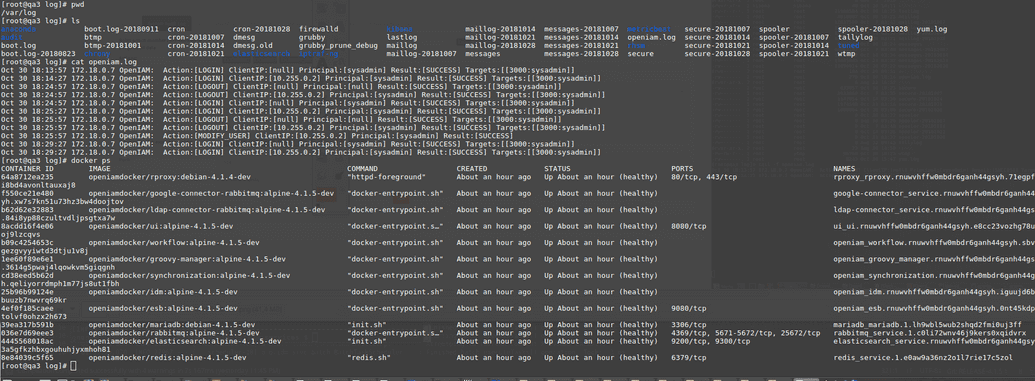
Syslog in Docker
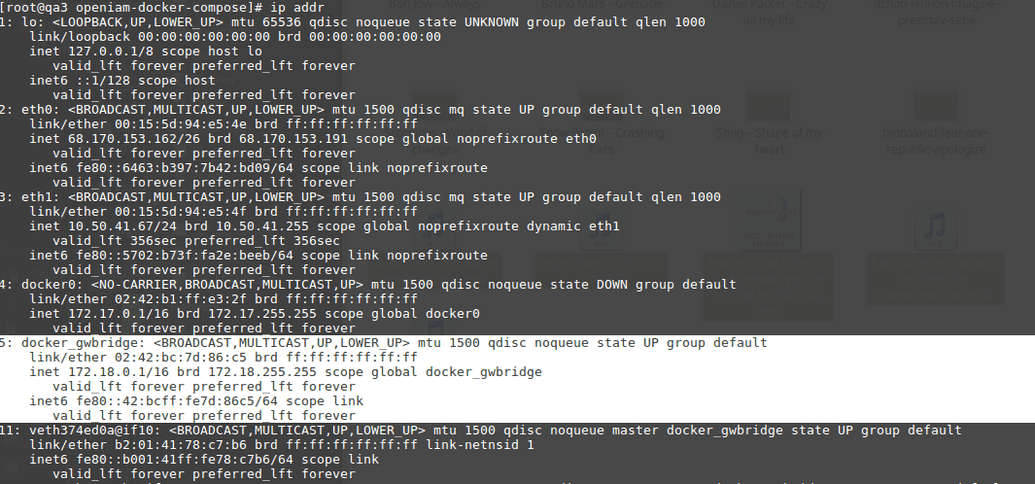
- Detect the Docker server IP for containers.
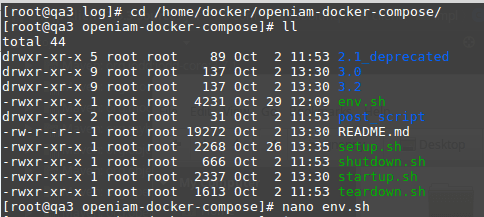
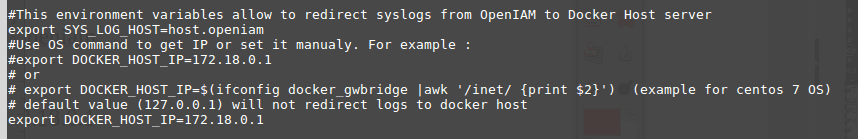
- Set properties in env.sh.
Host name:
export SYS_LOG_HOST=host.openiam
IP:
export DOCKER_HOST_IP=172.18.0.1
- Set the file for logs from OpenIAM in rsyslog:
nano /etc/rsyslog.conf
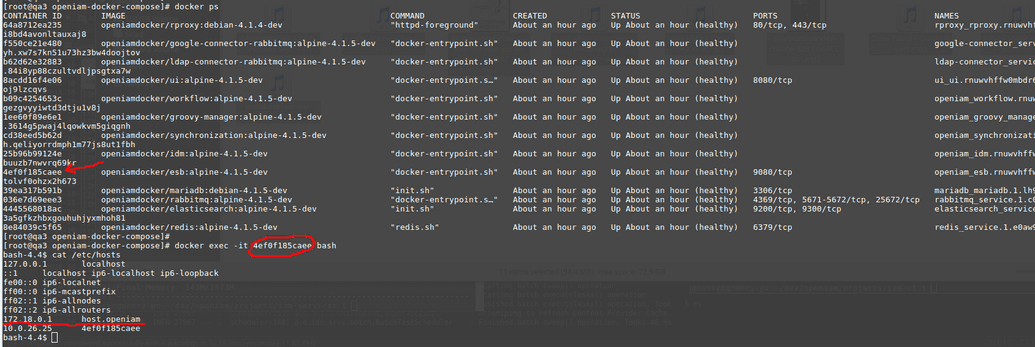
- Start Docker containers and check /etc/hosts:
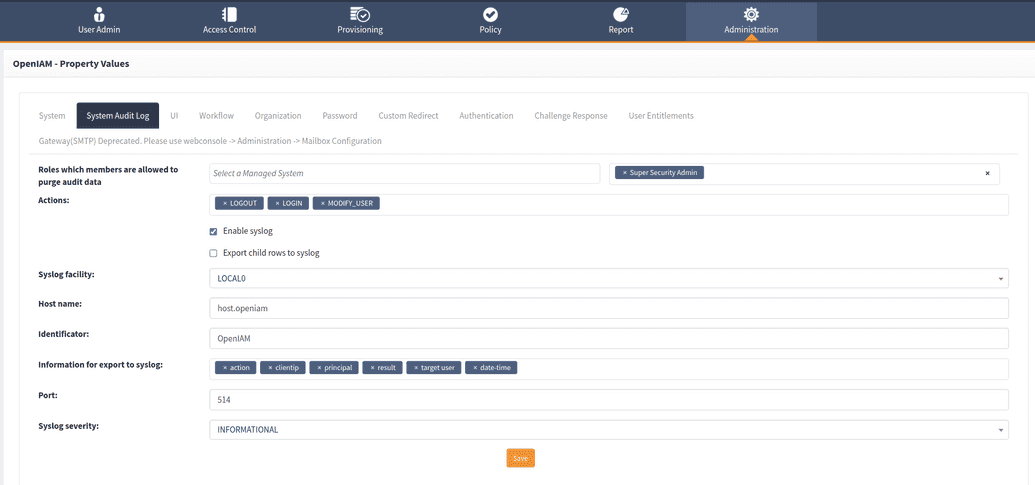
- Enable system audit log in OpenIAM properties:
After about 5 minutes, the logs will be sent to system logs.
- Check system logs on the Docker server:
Install rsyslog on Ubuntu
To install rsyslog on Ubuntu, follow the steps below.
- Run the following command.
sudo apt-get install rsyslog
- Now configure the rsyslog service to run in server mode. To do that, in the
/etc/rsyslog.conffile, uncomment the lines for UDP and TCP port binding, as shown below.
Provides UDP syslog reception
module(load="imudp")input(type="imudp" port="514")
Provides TCP syslog reception
module(load="imtcp")input(type="imtcp" port="514")
If you would like to limit access to a specific subnet, IP, or domain, add lines as below.
$AllowedSender TCP, 127.0.0.1, 192.168.10.0/24, *.example.com
To set the output file, you can add a row like the following:
local0.* /var/log/openiam.log
- Restart the rsyslog service for the changes to take effect by running the following command:
systemctl restart rsyslog.servicesystemctl status rsyslog.servicersyslog.service - System Logging ServiceLoaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/rsyslog.service, enabled)Active: active (running)root@22:/lib/systemd/system#
- Check your firewall configuration for
514/tcpand514/udpports to be open.
Configuration syslog export on K8 installation.
If Ubuntu is an external server, you only need to check the Enable syslog checkbox and set the correct external IP. This can be done provided your Kubernetes configuration has access to the internet.
To do so, go to web console > Administration > System configuration > System audit log tab and check the respective checkbox, as shown below.
Otherwise, if you are using an Ubuntu image in your Kubernetes, you need to configure Kubernetes to open port 514 on your Ubuntu image.
Example for creating a service for Ubuntu on K8.
- Create a syslog.yaml file with the following body:
apiVersion: v1kind: Servicemetadata:name: "ubuntu-syslog"namespace: "default"spec:ports:- port: 514targetPort: 514protocol: TCP- port: 514targetPort: 514protocol: TCPtype: ClusterIPselector:app: "ubuntu"
- Apply it to K8:
kubectl apply -f syslog.yaml
The service is created.