SAP UME connector
The user management engine (UME) provides a centralized user management for all Java applications and can be configured to work with user management data from multiple data sources. It is seamlessly integrated in the SAP NetWeaver Application Server (AS) Java as its default user store and can be administrated using the administration tools of the AS Java.
The UME adds business value by enabling you to leverage your existing system infrastructure by accessing user-related data on an existing LDAP directory, an AS ABAP system, a database of the AS Java, or any combination of these. In addition, it reduces administrative overhead by allowing you to perform centralized user administration.
SAP UME Connector can be local or remote. It’s a .war file that can be deployed in OpenIAM Application Server or in a different Application Server.
Connector usage
With SAPRP Connector you can do the following:
- Provisioning/Deprovisioning. The Connector can provision Users and s with all attributes that the target system supports. The list of the attributes can be found in Configuring the Policy Map section. In a common case, you can add any attribute in the Policy Map linked to the Groovy script and the attribute value will be provisioned to the target system.
- Group Management. The connector supports this feature, which is available for testing.
- Role Management.
- Reconciliation for
- Users
- Groups
- Roles
- Password Synchronization. The connector can set up user passwords and change them. SAP UME Connector uses SAP UME SPML interface to communication with SAP UME system.
Requirements for the SAP UME Connector
On the SAPUME server side:
- Add two roles in SAP UME.
- SPML_FULL_ACCESS_ROLE (SPML full access Role) with the following actions:
- SPML_Read_Action;
- SPML_Write_Action.
- SPML_READ_ACCESS_ROLE (SPML read only access Role) with the following actions:- SPML_Read_Action
- SPML_FULL_ACCESS_ROLE (SPML full access Role) with the following actions:
- Add two users in SAP UME.
- spmluser (SPML full access User):
- Role: SPML_FULL_ACCESS_ROLE.
- spmluser_readonly (SPML read only access User)
- Role: SPML_READ_ACCESS_ROLE.
- spmluser (SPML full access User):
Installing SAP UME Connector
Download and deploy jar using this link: http://download.openiam.com/customers/sia/sap-ume-connector-rabbitmq.jar.
Configure connection to SAP UME. Start with configuring the Managed System. Once the Connector has been defined in the Identity Manager, you can configure the connectivity to SAP UME. See the following screenshot.
To configure the properties of the Managed System, log in to webconsole and select Provisioning > Managed System > and select Create Managed System in case you are creating a new system or find an applicable out-of-the-box managed system and click Edit icon. For more information on Managed system creating and updating, refer to Managed system configuration page. Here, provide login and password for SAP UME user created above.
For example: http://10.1.11.58:50000/spml/provisioning.
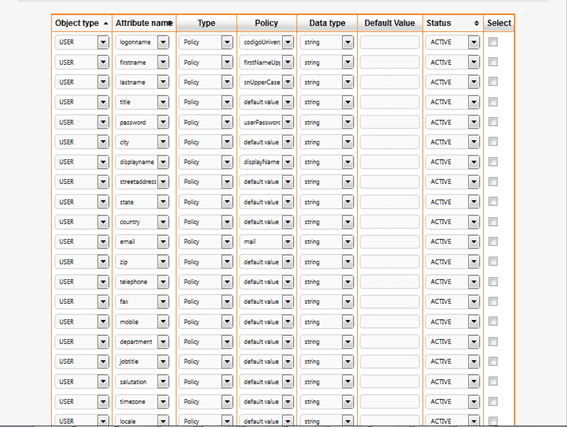
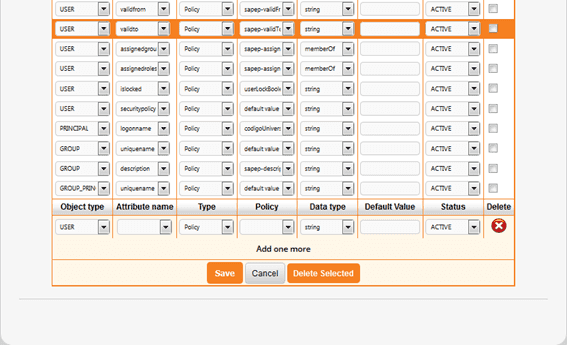
- Determine what attributes you need to pass to the SAP connector. Combined with the use of the Groovy scripting language, you can dynamically derive any attribute that is needed in SAP from the data maintained within OpenIAM. The screenshot below provides a sample mapping between rules in the Identity Manager, called attribute policies, and the SAP attributes. More details on the attribute policies and mappings can be found at the Policy map document.
Attributes allowed
| TAB | General Information | Note |
|---|---|---|
| Logon ID | logonname | |
| Last Name | lastname | |
| First Name | firstname | |
| E-Mail Address | ||
| Form of Address | salutation | |
| Language | locale | |
| Security Policy | securitypolicy | ('Default' or 'technical') |
| Unique ID | id | |
| Display Name | displayname | |
| Title | title | |
| Password | password |
| TAB | Account Information |
|---|---|
| Start Date of Account Validity | validfrom* |
| End Date of Account Validity | validto* |
| User Account Locked | islocked |
*Format Output in OpenIAM is "yyyy-MM-dd". Connector transforms this date format to date format allowed by SAP UME ("yyyyMMddHHmmss'Z'")
| TAB | Contact Information |
|---|---|
| Telephone | telephone |
| Fax | fax |
| Mobile | mobile |
| Street | streetaddress |
| City | city |
| State/Province | state |
| Zip/Postal Code | zip |
| Country | country |
| Time Zone | timezone |
| TAB | Additional Information |
|---|---|
| Position | jobtitle |
| Department | department |
| TAB | Assigned roles | TAB | Assigned groups |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assigned Roles | assignedroles | Assigned Groups | assignedgroups |
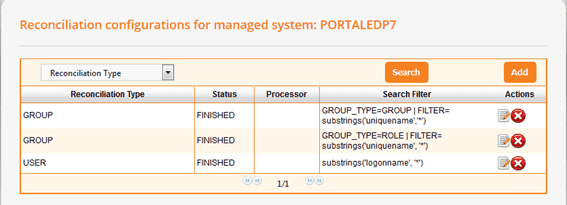
Reconciliation
More details on what is and how to configure reconciliation in OpenIAM can be found in Reconciliation section of documents.
Users
- Filter Operations:
equalityMatch,substrings. - Filter Logical operands:
AND,OR. - Complex filters: Filter can be formed with one or more clauses, but with only one logical operand (
ANDorOR). - Correct filters samples:
- substrings(
logonname,SAPUME). - equalityMatch(
logonname,SAPUMEUSU01) - equalityMatch(
logonname,SAPUMEUSU01) or equalityMatch(logonname,SAPUMEUSU02). - substrings(
logonname,a) or substrings(logonname,z) or equalityMatch(logonname,sapusu01).
- substrings(
- Incorrect filter samples:
- equalityMatch(
logonname,SAPUMEUSU01) or equalityMatch(logonname,SAPUMEUSU02) and substrings(logonname,z).
- equalityMatch(
Reconciliation can be full or Incremental. You can use UpdateSince MangedSysParam to indicate incremental mode and the date to filter last updates.
We also have a SAPSearchQuery.groovy developed, which checks if UpdateSince is informed and add "#TIMESTAMP#=yyyyMMddHHmmss" to the search filter. Here, the connector checks this string to make a full/incremental search. Sample Incremental Filter received by the connector if you indicate UpdateSince looks as follows.
substrings('logonname', 'SAPUME')#TIMESTAMP#=20150709131143Z
Connector detects #TIMESTAMP# and generates SPML filters as follows.
<dsml:filter><dsml:and><dsml:substrings name='logonname'><dsml:any>SAPUME</dsml:any></dsml:substrings><dsml:greaterOrEqual name='lastmodifydate'><dsml:value>20131008015052Z</dsml:value></dsml:greaterOrEqual></dsml:and></dsml:filter>
Groups and roles
Pattern for Groups and Roles filter looks as follows.
GROUP_TYPE=<groupType> | FILTER=<filter>- GROUP_TYPE --> "GROUP" or "ROLE"- FILTER --> Filter expression like user filter expression.
Sample filters are
- GROUP_TYPE=GROUP | FILTER= equalityMatch(
uniquename,Authenticated Users). - GROUP_TYPE=ROLE | FILTER= substrings(
uniquename,*).
Incremental reconciliation is not implemented for groups and roles.