Request / Approval
In most cases access is granted in one of two ways.
- Birthright rules.
- Requested access.
The first option, birthright rules, are rules that evaluate criteria such as job title, department, location or other attributes that are used in your environment. Based on these attributes access can be automatically granted. An example of a birthright access could be a rule that creates an AD account for the user, puts them in the right OU, sets the required group memberships network, drives and creates a mailbox. Birthright rules enable access to be applied in a consistent way and can reduce the amount of time needed for onboarding transfers and terminations. Granting access by a birthright rule is described in detail in this document.
The second way to gain access is by creating a request. Here, either the employee or their manager can create a request for an account or entitlements. If the access requires authorizations then one or more people may be required to approve the request. Once all the authorizations have been obtained the system can either automatically provision access or a notification can be sent to the service to ask to have someone manually provision the access. Even if access is provisioned manually there are compliance benefits to this process.
This document deals with the second access granting option - defining a request/approval model via service catalog.
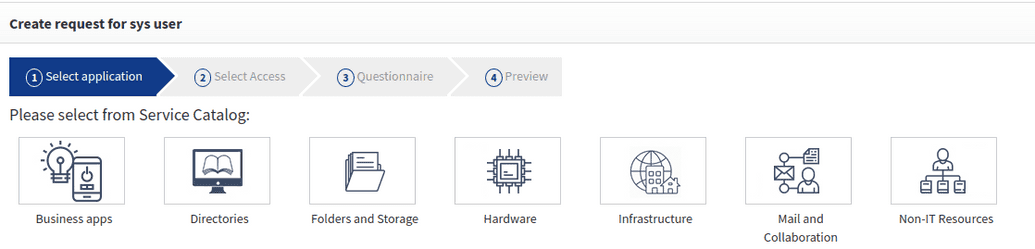
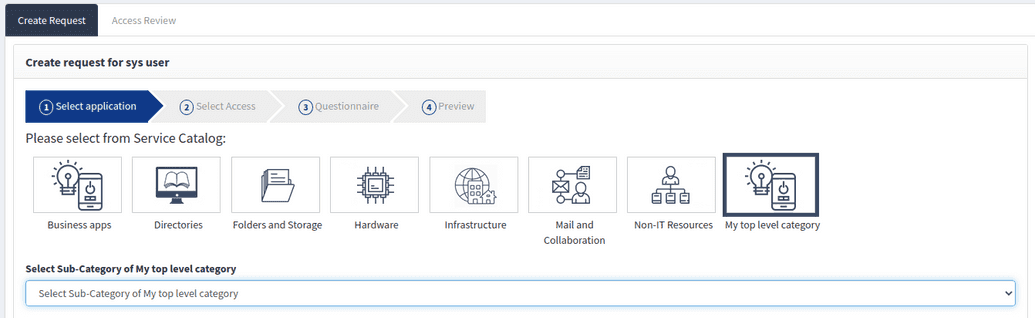
A service catalog in the SelfService portal is the shopping-cart based. Using the catalog, users can search, find entitlements or objects that they need and then create a request. Upon approval, access will be granted.
To implement a service catalog in OpenIAM, we need to do the following:
- Define a categorization / classification structure within which users will find their applications and entitlements.
- Define the approval flow.
The following video tutorial provides an introduction to workflows.
The sections below will describe how to configure each of these.
Define a categorization structure
If you goto Selfservice > Create request for myself > Select from service catalog you will see that the catalog is structured by categories, as shown below. This structure is a default model and you can customize this model to meet your organization's needs. This categorization structure and appropriate naming can have a significant impact on how easily end-users are able to navigate the catalog and find what they need.
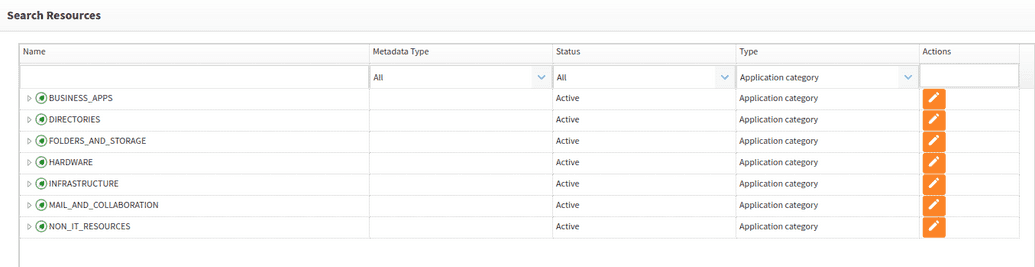
Categories are a type of resource, and all resources regardless of type are part of the open IAM Access Control model. To view the existing category structure, go to Webconsole > Access Control > Resource and filter by Application Category as shown below.
You can modify or remove these categories based on your needs.
Creating a new category
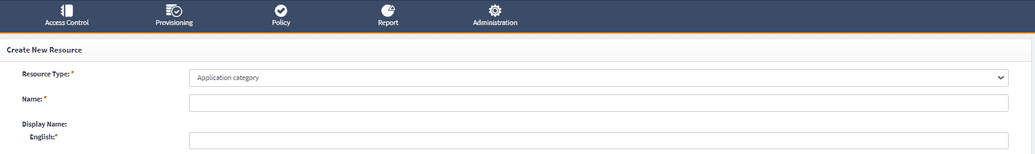
To create a new category goto Webconsole > Access Control > Resource and click Create New Resource in the side menu bar.
Complete the fields which are shown in the table below.
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Resource Type | Select Application category from the dropdown. This setting determines which type of resource we are creating. |
| Name | Name of your category. This value can be any short descriptive name. |
| Display name | This is a value that end-users will see. It should have a short descriptive name which should be meaningful for end users. This field has been localized and you should complete the localization for the languages that you need to support. |
| Status | Flag which determines if this resource is active (visible) or inactive (hidden from users). |
| Is Visible | Determines if this resource is visible or not from end-users. |
If you need to support multiple languages, then you should fill out the display name values for the languages that need to be supported.
Save your category. You should see it appear in SelfService as well.
Create a child category
In some cases, when working with a large number of applications, you will want to nest your category structure. To create a child category
- Create a new category like it is described in the previous step.
- Find the parent category by going to webconsole > Access control > Resource and then search for the name of the category.
- Click the
Actionsbutton to view the resource details. - From the side menu bar, click
Entitlements. - Right click on
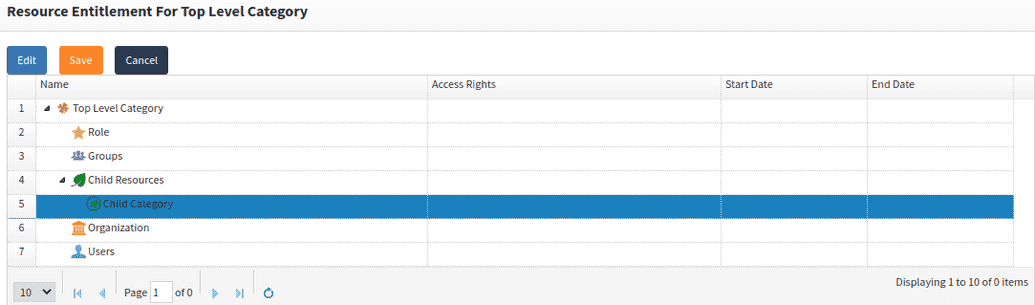
Child resourceand then clickAdd. - From the dropdowns, first select
Application categoryand then the name of your category in the second dropdown.
The parent-child relationship should appear like in the example below.
In the SelfService portal, the addition of a child category in the service catalog will appear as shown below.
Associating the application with a category
The next step is to associate an application to a category. As discussed in an Application onboarding section, applications that are involved in user provisioning are represented as either managed systems or manual managed systems. Each of these is a type of resource. Let us assume that you have already created a resource.
To associate an application to a category
- Go to Provisioning > Managed System and find the application that you want to work with.
- Open the details by clicking
edit. - Scroll down the page and find the drop down for categories
- Select your category and click
Save.
Now you can define an approval flow.
Define approval flow
OpenIAM allows you to define the approval flow at either the application level (Managed System or Manual Managed System) or at the application entitlement (Group, Role, Resource) level. When working with applications which have hundreds or thousands of entitlements, it may be better to define at the approval flow at the application level and then override that flow at the entitlement level if needed. This approach is often more maintainable than defining approvers only at the entitlement level.
You also need to define how many steps are required in the approval process and who will be the approver, as well as to determine if there is a need to define reminders or escalations for situations where the approver does not respond in a timely manner.
To define approvers follow the steps below.
Application level approval
To configure an approval flow on application level
- Go to Webconsole > Access control > Resource.
- Filter by either
Managed SystemorManual Managed systemin the Type column. - Find the name of your application by searching in the Name column.
- Click on the button in the Actions column to see the application details.
- If the approval flow will require approval by an application owner or admin, then you need to define that. On the screen you can select either a single owner or a group of owners in the
Resource ownerline on the details screen. You can select a group when anyone in a group can be an approver. - Save your changes.
- Define the approval flow
- Click on the
Approval Associationsmenu from the side bar. - Click on the
New approver stepon the screen below. It will open up a row where you can define the approver.
- Click on the
Complete the fields in the approval flow as described below
- Approver - Select the type of approver followed by the name of the approver. The table below describes each of the approval options.
- Notify on Approval - Select who should be notified after this step has been approved.
- Notify on Reject - Select who should be notified if this step is not approved.
- Request service level agreement parameters
- 1* - Number of reminders which should be sent to the approver to complete their task in a timely manner.
- 2* - Number of days which should elapse before sending out a reminder.
- 3* - Calculated values from 1 and 2 which indicate the maximum amount of time allowed to complete this step.
- Save your configuration (must be done independently of the save operation on the page).
To add additional approval steps, simply save the first approver and click on the New approver step as shown above.
Approver Types
| Type of Approver | Description |
|---|---|
| Supervisor | The manager of the person for whom this request has been created. Note, if the manager has submitted the request, then approval for the manager will be skipped as it is assumed that the manager wanted to grant this access when creating the request. |
| User | Select the user that should be the approver. |
| Group | Group of people who should be the approver. Anyone in the group can claim and approve. |
| Target user | Target user is the user for whom this request was created. |
| Application owner | Owner that is defined on the managed system or manual managed system. |
| Application admin | Admin that is defined on the managed system or manual managed system. |
| Entitlement owner | Owner that is defined on the entitlement (group, role, resource). |
| Entitlement admin | Admin that is defined on the entitlement (group, role, resource). |
Entitlement level approval
To configure an approval flow on application level
- First enable entitlement level approval:
- Go to Webconsole > Administration > System configuration.
- Go to the
Workflowtab. - Enable the checkbox labeled
Use approver association or role/group instead of resource. - Determine the type entitlement that you need to find - Role, Resource, or Group.
- Go to Webconsole > Access control > [your entitlement type].
- Filter by the managed system name in the Managed System column.
- If you application has several types of entitlements, you can further filter by the Metadata type in the Type in column
- Find the name of your entitlement by searching in the Name column.
- Click on the button in the Actions column to see the entitlement details.
Global Default approver
You are not required to provide an approver for each application or entitlement. There are two ways to configure the system:
- An approver is not defined then it means that no approval is required in request for an application or entitlement will be automatically approved.
- To set a global default approver.
In the second case when no approver has been provided then we can use the global configuration. A default approver at the system level can be helpful in catching potential configuration issues such as a configuration that has been overlooked. These configurations are defined in the workflow section of the system configuration menu. To configure a global approver.
- Go to webconsole > Administration > System configuration.
- Then go to the `Workflow`` tab. Here you will see a variety of system level configurations related to workflows.
- Find
Default workflow approverproperty. - Remove the current value and then search to find the user needed.
- Save your changes.
More on approval flow can be found in this document.
Manual tasks
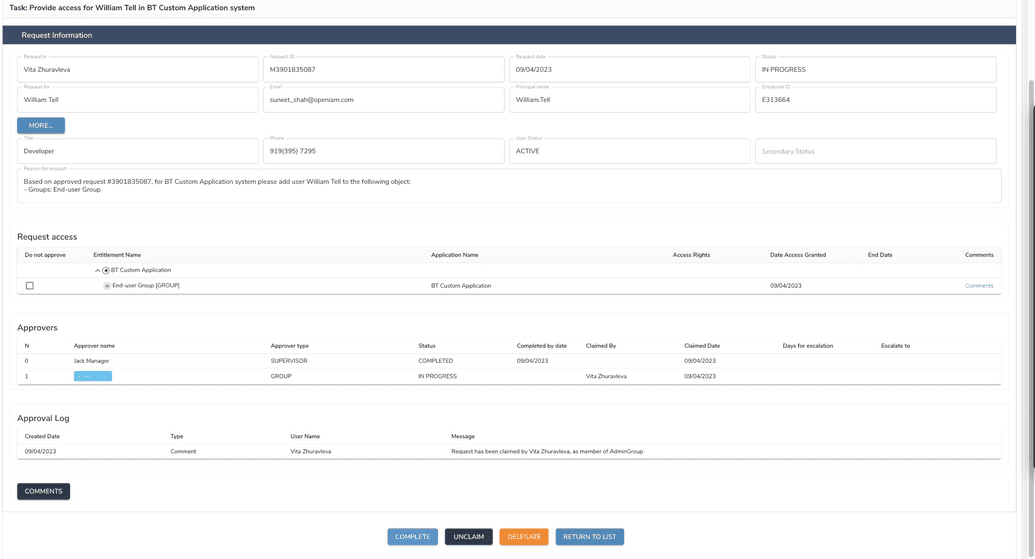
Manual task is generated when request for access/revoke access to manual managed system was approved.
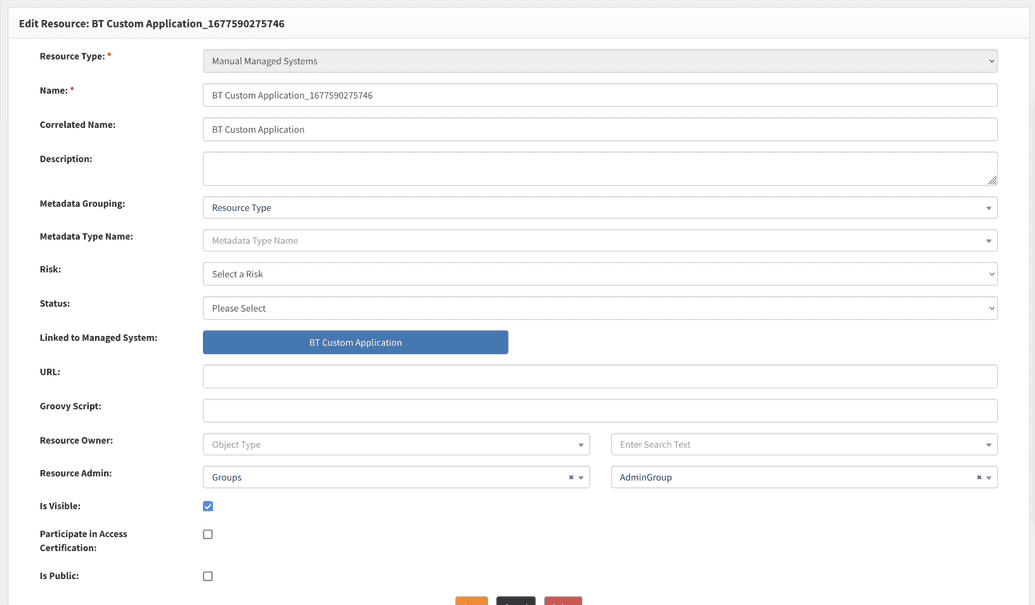
Manual tasks will be assigned to an admin of resource for manual managed systems, as shown below.
This managed system has an appropriate resource.
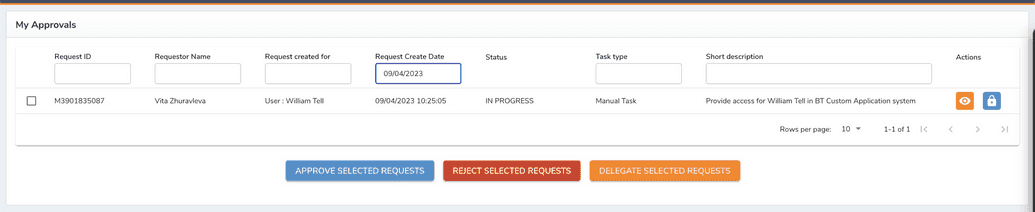
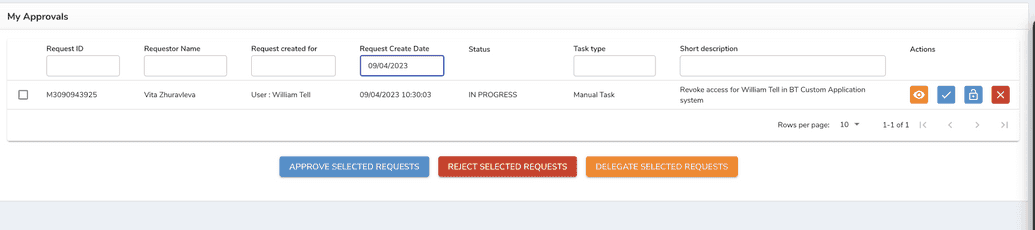
After a request for access was approved, the admin group receives a task to complete.
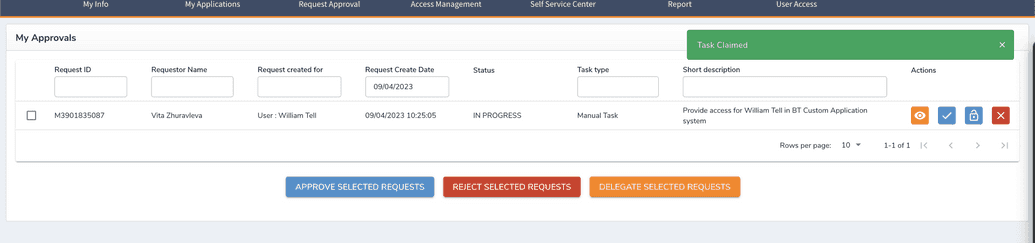
Since it's a group of admins, one of the members has to claim the task first. After the task was claimed.
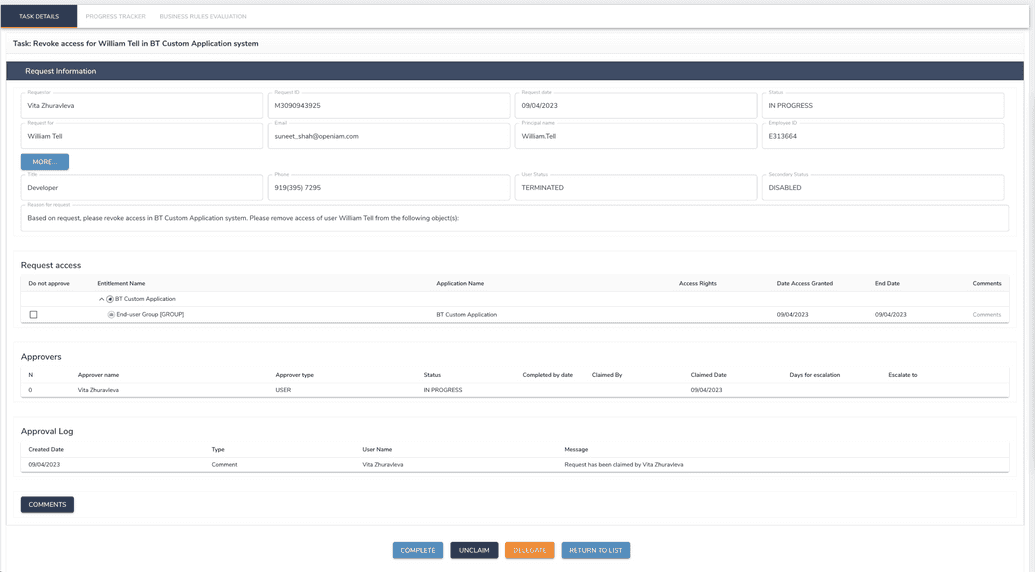
Here, the admin who claimed the task can complete it in the manual system and in OpenIAM (at this moment entitlement was already assigned to a user, manual task represents only the action the admin has to do to provide/revoke access in system manually).
An example of a task for admin when a user with access to manual system got terminated is given below.